Preview
Parallel software testing is a very difficult task on the technical side. This process is more complicated and convoluted than testing of parallel programs and their components.
A developer should remember about all pitfalls when testing the program code that he/she created, about the total used technologies and wide tools set, which can be used during its (code) designing.
Let’s start from the beginning.
As we know, during any software development, 3 main stages of product testing and debugging can be distinguished.
In practice, concepts of “testing” and “debugging” aren’t very different by their meaning. It’s connected with the fact, that right after you find an error while testing, you need to debug the program for its further fixing.
Also, debugging of the product can be named black-box testing. Often debugging stage is considered as a simultaneous searching for a bug and its fixing.
Testing parallel programs – is a special method of bug searching inside the software with the help of special tools, also, it’s an analysis of software productivity during its usage by the final group of users.
Debugging – is searching for errors in the program code, which were discovered during software testing for its further fixing. “Debugging” is special using of tools and methodologies, which help to track the current state of the software at the stage of its development and fixing.
Debugging the parallel programs – is a hard process that needs a total exactitude, attention and wide set of various tools.
Before starting the debugging, you have to fix the bug. Also, there’s a group of debugging methods, which allows us not only to find errors but to trace them immediately.
Let’s proceed with testing.
Difficulties of Testing Parallel Programs
Testing parallel programs is a real deal. During parallelization, it can be difficult to find bugs, because of the non-determinacy of parallel utility functioning.
Even if the bug was found, sometimes it’s difficult to reproduce it for the second time.
Also, after the modification of program code, it’s very hard to be sure that the bug was really fixed, but not only “hidden”. To all this, we can give another meaning: bugs in the parallel testing are called “heisenbug”.
Heisenbug – is a special interpretation, which is used in the programming for detailed error review, that can disappear or modify its technical characteristics during its search.
Such concept is a simple play on words and came from the physical concept “Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle”, which on the simple level, is considered as a process of monitor object valuing after its monitoring, that are in a quantum mechanics. In testing, you can often see a concept “floating error”, which meaning is similar to heisenbug.
An illustrative paradigm of its regularity – are bugs, which can be found in the final software version, and weren’t noticed in the debugging mode, or defects, synchronized in the multithreaded product or module.
All this means that the basic task of parallel testing is an actual problem of quality diagnostic tools development, which has minimal influence on the behavior of the software or which would create all necessary conditions for bug appearing.
Further, we’ll look at traditional methods of testing.
The Methodology of Searching for Bugs in Parallel Modules
Such a methodology, just like sequential testing, can be easily divided into the dynamic and static analysis, model-based testing and the proving of the correctness of product functioning.
Dynamic analysis is a necessity to launch the product and to perform a defined chain of sustained actions. Its task is to define the formula of software incorrect conduct.
A process of sustained actions can be established by a human during manual testing as well as on the basis of the automated tools, that are doing load testing, for example, test for verifying the integrity of the information.
In case of parallel program testing, there’s a need to emphasize the tools, like Intel Thread Checker, with the help of which it’s possible to supply a source program code of some utility with a lot of monitoring and protocoling means, that can find mutual lockups (visible and hidden ones).
Static analysis interacts only with a scripted code and doesn’t need its launching. The main advantage of such a method is a full analysis of all activities.
Moreover, in the field of parallel programming, static analysis methodology is used really seldom and has not so many tools, which are connected with an exploratory category, but not with commercial releases.
Unit testing is an automated generation of the tests on the defined criteria. Searching for the bugs on module basis allows QA specialist to substantiate technically the absence of errors in the tested part of the program code, on the basis of rules of info transformation chosen by a developer.
In particular, you can use the proven KISS tools, designed in the Microsoft Research company, for similar utilities’ aims on the basis of C programming language.
All methods, that were listed above, have a lot of significant disadvantages, which don’t allow the testers to rely fully upon them while performing parallel testing/during the parallel testing of the developed software.
Dynamic analysis requires the launching of many apps and utilities, is very “sensitive” to execute the environment and significantly reduces the module action speed inside the developed product.
It’s very difficult to cover the whole part of the parallel program code with tests. Possibility to record officially the race condition can be only in case if it was held in the current session of program functioning.
In other words, if the components of dynamic analysis “say” that there’re no bugs, you as a tester can’t be fully sure about that.
From the all, listed above, there’s a regularity that usage of only one approach to parallel component testing is non-effective, and it’s better to use 2-3 methods for testing the same program product or system.
Modern systems – a variety of tools and methods
Since, in the times of solving the problem: how to widen the productivity of the software, developers chose multi-core criteria, it has led to high-speed development of different tools for web components designing.
For similar multi-core systems, it’s typical to use such methods of deployment as OpenMP, instead of classical MPI, or traditional methods of parallelization, which can be found inside some operation systems (beginthread, fork).
Anyway, new technologies make us use only new and actual tools for their technical support.
It’s recommended continuously to follow the new versions of support systems for parallel programming modules, which appear on the world software markets on an annual basis. With their help, we can reduce workload while doing parallel testing, as well as qualitatively adapt utilities for optimal usage in the parallel environment.
A Few Words About OpenMP Technology
Essentially, OpenMP technology is fully programmed to parallelize gradually the selected parts of the program code. With its help, tester and programmer can divide the product into blocks of program code in the parallel form.
It’s enough to set necessary directives on the parts, which are considered as the most critic ones during software performance.
As a result, the parallel program code is structured and doesn’t depend anymore on the state of other software parts, and it means that QA specialist can do a quality review of its functional validity to multiple use.
A couple of years ago the field of static analysis on the OpenMP base wasn’t totally implemented by programmers. One of the examples is compilation Sun Studio, which ran a diagnostic on the selected parts. Static analysis VivaMP was able to occupy properly an unoccupied niche.
Tools VivaMP – is a modern extremely specialized utility, that was specially created to find the bugs inside the parallel designed programs on the methodology of OpenMP, based on C or C++.
This analyzer can find visible defects and inform tester about “dangerous” or “weak” code.
A good example is a method to find one variable for parallel threads creation, without a need to do the synchronize testing:
A good example of testing the potentially dangerous part of program code is the practice to use flush for a pointer. It’s easy to make a mistake if you forget that flush function will be interpreted to the pointer, but not to the information, it has referred to. In the end, this code can be valid or invalid:

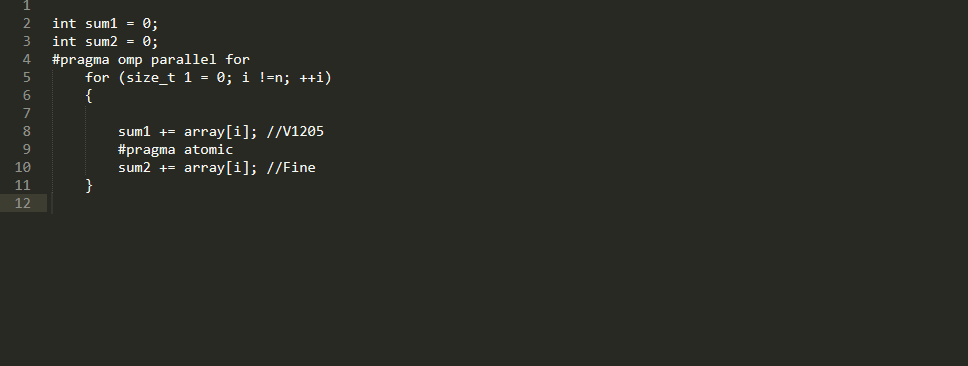
In the next making of complier VivaMP, the functionality of testing the connectedness with the finding of non-effectiveness of the program code development will be fully completed. For example, will modules be counted as critical ones, if firstly a quick directive atomic was used:

Instead of Conclusion
Quality control companies have to understand that nowadays in the world there’re many different forms of parallelization of the developed software.
But for making the commercial group of utilities and components, which firstly used multi-core processors, completely another methods and approaches to development are needed; which will be different from the one, used during successive components development.
We hope, that our article can help to understand those difficulties, which constantly appear in the process of parallel web product and components development; and testers with programmers will be able to use only effective programs and methods in the future.

