Also, JIRA is usually used to track bugs and find defects. The tool was designed by Australian company called Atlassian. JIRA was initially released in 2002.
The name “JIRA” looks like abbreviation but it is not the case. However, actually, JIRA — a downsized version of Gojira, Japan pronunciation for Godzilla. In fact, it is a reference to Bugzilla, the major competitor of JIRA.
Conceptual concepts of JIRA — Issue, Project and Workflow.
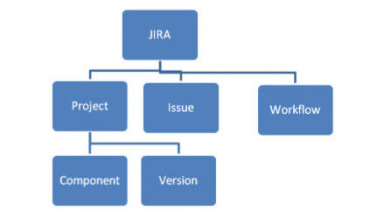
JIRA scheme
Let us find out what these main concepts mean.
Issue of JIRA
In reality, everything that can be created and tracked with JIRA feels like an issue:
- Bug.
- Project issue.
- Form of request.
- Information card.
- Task creation.
Now it is time to understand how to create an issue in JIRA.
In order to create an issue the user should have permission to create tasks in this project.
Steps in creating an issue:
- Log in to JIRA account and go to toolbar.
- Push the button “Create” in the upper part of the screen so that the dialog window “Create Issue” can appear.
- Fill in the all mandatory fields.
Project
Here you should choose the right name of the project.
The main attributes of the task: Statuses, Resolutions and Priorities.
- Issue Status indicates the progress of the project.
- Resolutions show us how the issue can be closed.
- Priority defines the issue’s importance relating to other issues.
Issue types
In the menu “Issue Types” you can see all types of the elements which can be created and tracked with JIRA.
In order to meet the needs of your projects and commands, JIRA apps come with default issue types.
Sub-task
Sometimes it is necessary to divide the main task into several simpler and smaller tasks. You may assign and track these tasks individually.
JIRA Workflow
It is a set of statuses and transitions through which an error / issue / problem passes across its entire lifecycle. In fact, it represents internal processes within your organization.
There are 5 phases of issue life cycle:
- Open problem.
- Resolved problem.
- Problem in hand.
- Repeat problem.
- Close task.
There are active and inactive workflows. If the workflow is now used in one or several projects, then it is an active workflow, otherwise it is an inactive workflow.
Do you want your customers to be satisfied with software apps you develop? What about using beta testing services? Specific group of people will be checking your products to make sure that they are ready to be successfully distributed to the wider public.

